受精卵が卵割して、着床し、3胚葉ができる頃にはいろいろな膜に覆われたり、腔ができたりして、しかもその構造の名称が複数あったり時期によって変化したりいろいろ混乱しやすいので、纏めておきます。発生の順番で出来上がるものを覚えていったほうが、流れが掴みやすくて頭に入りやすいと思います。
両生類では、嚢胚形成(原腸胚形成)の時期に細胞が外肺葉から中に潜り込んで中胚葉ができ、外胚葉、中胚葉、内胚葉の三葉が確立して、それぞれが各臓器に分化するという単純なストーリーなのに対して、哺乳類の発生では、胚になる部分(intraembryonicもしくは単にembryonic)と胚にならない部分(extraembryonic)との区別が大事で、両生類で学んだことは哺乳類ではintraembryonicに関することが対応しており、そこがわかっていないと名称で混乱します。胚盤胞(blastocyst)(両生類の胞胚(blastula)に相当)の時期には外側の部分と内側の部分(内部細胞塊)に分かれていますが、胚になるのは内部細胞塊の一部です。内部細胞塊はepiblastとhypoblastに分化し、epiblastの部分が胚になる(すなわちembryonic ectoderm, embryonic mesoderm, embryonic endoderm)ということを押さえておく必要があります。hypoblastは胚への寄与がありません。
自分が混乱したのは、両生類と違って、哺乳類では(embryonic) endodermは嚢胚形成の時期にepiblastからhypobalstのほうにもぐりこんで移動してきた細胞だということを知らなかったからです。epiblastから移動してきた細胞がhypoblastの細胞と「置き換わる」ことにより、それまでhypoblastだった部分は、endodermになります。hypoblastの細胞がembryonic endodermになるわけではありません。このことを知らずに教科書の図を見ていると、混乱させられます。
名称に関しての注意事項として、なになにmesoderm、なになにendodermといった言葉が多数出てきますが、それがどの時期のどの細胞由来のものかを整理しておくことが大事ということがあります。例えば、Extraembryonic mesoderm 胚外中胚葉というものはparietal endodermからできてきますが、parietal endodermはhypoblast由来です。「mesoderm」や「endoderm」という言葉が含まれていますが、これらは両生類のところで学んだmesodermやendodermとは別の概念なんですね。初めてこれらの言葉を見ると紛らわし過ぎて本当に混乱しました。
同じ言葉を使いつつ概念を区別をするために、primitive、definitiveという形容詞が使われることもあります。primitive endodermはendodermじゃないから、primitive (原始の)endodermと呼ばれ、本当のendodermはdefinitive endodermになります。definitiveは日本語に訳しにくですが、原始じゃなくてというわけです。
The inner cell mass of the blastocyst has differentiated into epiblast and hypoblast (primitive endoderm) prior to implantation.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3788819/
hypoblastはendodermじゃないというのは研究が進んでわかったことみたいです。それで呼称が変わったわけですね。古い文献だと混同した使われ方をしているのだと思います。
In mammals, the existence of primitive endoderm and its association with both the extra-embryonic yolk sac and the embryo proper had been noted at the end of the 19th century. The primitive endoderm underlying the primitive ectoderm/epiblast became known as visceral endoderm, whereas that on the maternal side became parietal endoderm, as first recognized by Duval and Sobotta (Duval, 1891; Sobotta, 1911)
However, many years passed before it became clear that the primitive endoderm is replaced by definitive endoderm, which mainly gives rise to the lining of the gut. The first clear experimental demonstration came from the careful experiments of Bellairs, who combined electron and light microscopy, cell marking and experimental embryology. Bellairs established that the deep layer of ‘endoderm’ present in chick embryos before the appearance of the primitive streak contributes to the extra-embryonic yolk sac stalk (Bellairs, 1953a; Bellairs, 1953b). Thus, the early chick embryo contains a transitory, extra-embryonic cell layer at its ventral surface. Its name, ‘endoderm’, was replaced by the term ‘hypoblast’, to distinguish it from definitive gut endoderm, which, as shown by Bellairs, is derived from the epiblast via ingression through the primitive streak, replacing the hypoblast.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3283119/
ヒトとマウスで、epiblastとhypoblastの分離のメカニズムに関して相違もあるようです。マウスの結果がそのままヒトに当てはまらないこともあるわけですね。
Hypoblast cells form an extraembryonic cell layer on the surface of the inner cell mass and faces the blastocoelic cavity. It gives rise to the visceral and parietal endoderm. The hypoblast cells are separated from the epiblast layer by an extracellular basement membrane. Notes These cells are evident from E7 in mouse development. Lineage marker transcription factors are: SOX17, GATA4, GATA6, PDGFRa. Human hypoblast differentiation differs from that observed in mouse, rat and cow embryos in their absence of appreciable Laminin expression in the presumptive hypoblast and downregulation of GATA6 in a subset of SOX17-expressing cells. This, in addition to different reactions to FGF/Erk signaling inhibitors, suggests that the human hypoblast may segregate by unique mechanisms.
以下、大雑把にヒトの発生のイベントやターミノロジーをまとめておきます。
fertilized eggs 受精卵
受精卵は一つの細胞です。これ以上シンプルなものはない、分かりやすいものです。
morula 桑実胚
受精後3日目には細胞分裂を何回か生じて16細胞くらいになると、桑の実のような粒粒にみえる時期なので桑実胚と呼ばれます。
compaction コンパクション
8細胞期から16細胞期にかけて、外側のblastomers 割球が強く接着して、割球が外に飛び出してでこぼこしていたのがなくなり表面が滑らかに見えるようになります。この変化をcompaction コンパクションと呼びます。
- Carlson Fig.4.2
- No evidence of involvement of E-cadherin in cell fate specification or the segregation of Epi and PrE in mouse blastocysts Katarzyna Filimonow,Nestor Saiz,Aneta Suwińska,Tomasz Wyszomirski,Joanna B. Grabarek,Elisabetta Ferretti,Anna Piliszek,Berenika Plusa ,Marek Maleszewski Published: February 8, 2019 PLoS One. 2019; 14(2): e0212109. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212109
桑実胚からblastocyst 胚盤胞ヘ:栄養外胚葉と内部細胞塊への分化
受精後4日目には数十細胞にまで分裂しており、この時期から着床前までの時期の胚のことはblastocyst 胚盤胞と呼ばれます。内側が空洞で袋状になっているので「胞」なんですね。カエルの発生学ではblastula 胞胚と呼んでいたと思います。哺乳類と両生類では、使う言葉も違うようです。
- Blastocyst development embryology.med.unsw.edu.au (Greek, blastos = sprout + cystos = cavity) or blastula, the term used to describe the hollow cellular mass that forms in early development.
- 受精卵(胚・胚盤胞)のグレードについて|評価のポイントを解説 木場公園クリニック 5日目(採卵後5日後)から着床前の胚を胚盤胞(blastocyst)と言います。 胚盤胞は、内細胞塊(inner cell mass)、栄養外胚葉(trophoblast)と胞胚腔(blastocyst cavity)で構成され、 70-100個の細胞からできています。 内細胞塊は、身体のあらゆる細胞に分化します。 一方、栄養膜は胎盤や羊膜などの胚外組織に分化します。
blastocoel / blastocyst cavity胞胚腔(ほうはいくう・ほうはいこう)
blastocoel 胞胚腔(ほうはいくう・ほうはいこう)は、blastocyst 胚盤胞の内側の空隙の部分を指します。英語だとブラストシールといった発音。日本語で漢字「腔」の読み方は、「くう」と「こう」の両方あるようです。口腔(こうくう)からすると「くう」がいいように自分は思うのですが。
- https://lsd-project.jp/cgi-bin/lsdproj/ejlookup04.pl?opt=c 胞胚腔
inner cell mass (ICM) 内細胞塊 / embryoblast 胚芽
blastocyst 胚盤胞は、2つの領域に分かれています。
- https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php
胞を作っている部分が、trophoblast 栄養外胚葉で、その内側に細胞の塊が存在しており、inner cell mass 内細胞塊と呼ばれます。inner cell mass 内細胞塊は、embryoblast 胚芽(はいが)とも呼ばれます。将来、ヒトの体になるのがこのinner cell mass 内細胞塊です。
- 医学部発⽣学(4):三胚葉形成〜軸形 2018年7月6日 医学系研究科附属創⽣応⽤医学研究センター⻑ 脳神経科学コアセンター⻑ 発⽣発達神経科学分野教授 ⼤隅典⼦
trophoblast 栄養外胚葉
trophoblast 栄養外胚葉は、ヒトの体の構造には寄与しません。
zona pellucida 透明体
blastocyst 胚盤胞の外側部分には、透明なゼリー状の物質が存在していて、zona pellucida 透明体と呼ばれます。
- https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php?title=Blastocyst_Development#/media/File:Human_embryo_day_5_label2.jpg
- https://minerva-clinic.or.jp/academic/terminololgyofmedicalgenetics/tagyou/zona-pellucida/
- Carlson Fig.4.1
内部細胞塊の分化:epiblast 胚盤葉上層とhypoblast 胚盤葉下層
内部細胞塊は2つの細胞集団に分かれます。一つが、epiblast 胚盤葉上層で、こちらがさらにない胚葉、外胚葉、中胚葉に将来分化して人の体を構成することになります。それに対してhypoblast 胚盤葉下層は、一部はそこに留まりますが多くは栄養膜に沿って胞胚腔の壁際に広がり,yolk sac 卵黄囊 (primary yolk sac)と呼ばれる袋を形成します。
- https://www.yodosha.co.jp/jikkenigaku/keyword/2001.html
- http://www.chugaiigaku.jp/upfile/browse/browse3399.pdf
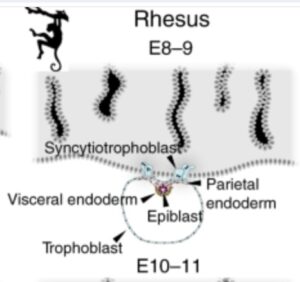
hypoblastからvisceral endodermとparietal endodermへの分化
hypoblastの細胞はvisceral endodermとparietal endodermとに分化し、parietal endodermはtrophoblastの壁の内側を広がって袋を形成します。この結果、卵黄嚢ができます。
The hypoblast forms a squamous epithelium covering the epiblast58 and expands beyond the epiblast margin. At this stage, hypoblast cells diversify into visceral and parietal endoderm (Fig. 2). Visceral endoderm overlies the epiblast and gives rise to a cuboidal epithelium. The peripheral hypoblast cells become parietal endoderm, which forms an inner lining of the trophoblast. Both visceral and parietal endoderm contribute to the primary yolk sac55,59.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-17575-w
- Carlson FIG.5.4、FIG.5.2
Extraembryonic mesoderm 胚外中胚葉
受精後12日目ごろに、parietal endoderm由来のExtraembryonic mesoderm 胚外中胚葉というあらたな細胞が出現します。Extraembryonic mesoderm 胚外中胚葉の細胞は、primary yolk sacの膜(Heuser’s membrane)とcytotrophoblast(blastocystの壁だった部分)の間の空間(すなわちblastocyst cavity胞胚腔)を満たすようになります。
- 中外医学社 基礎編―人体発生― http://www.chugaiigaku.jp/upfile/browse/browse3399.pdf
- Larsen FIG 2.2 および説明文
yolk sac 卵黄囊(らんおうのう)/exocoelomic membrane/Heuser’s membrane
上で説明したように、yolk sac 卵黄囊は、内部細胞塊から分化したhypoblast 胚盤葉下層がさらにparietal endodermの細胞に分化してそれがblastocoel 胞胚腔の壁(trophoblast 栄養外胚葉、栄養膜)に沿って移動して広がっていって膜を形成したものです。「囊」(のう)は袋の意味。この段階でできた卵黄脳は、primary yolk sac 原始卵黄嚢あるいはexocoelomic membraneあるいはHeuser’s membrane(ヒューザー膜)と呼ばれます。primary yolk sacはこのあとsecondary yolk sac の形成に際して押しやられて消滅します。secondary yolk sacがその後も残り続けます。
- 中外医学社 基礎編―人体発生― http://www.chugaiigaku.jp/upfile/browse/browse3399.pdf
- Carlson FIG.5.2
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heuser%27s_membrane
- Larsen’s human embryology 2:Second Week Becoming Fully Bilaminar and Implanting Heuser’s membraneに関する記載はCarlsonの教科書にはありませんでしたが、Larsenの教科書では言及されていました。
amnion(羊膜)とamnionic cavity(羊膜腔)
epiblast 胚盤葉上層はamniotic membrane(羊膜)になる部分とそのままとどまって胎児になる部分とに分化します。epiblast 胚盤葉上層の内部に空隙が生じ、その空隙がamnionic cavity(羊膜腔)となります。amnionic cavity(羊膜腔)はこのあと大きく広がって胚を包む袋となり、胚発生は羊膜につつまれて羊膜腔の中で進行することになります。
- http://www.chugaiigaku.jp/upfile/browse/browse3399.pdf
- Carlson FIG.5.2 および本文 “The epiblast contains the cells that make up the embryo itself, but extraembryonic tissues also arise from this layer. The next layer to appear after the hypoblast is the amnion, a layer of extraembryonic ectoderm that ultimately encloses the entire embryo in a fluid-filled chamber called the amniotic cavity (see Chapter 7).”
二層性胚盤 bilaminar embryonic disc
amnionic cavity(羊膜腔)とyolk sac 卵黄囊という二つの袋が形成されるとその間に、epiblast 胚盤葉上層とhypoblast 胚盤葉下層の2層の円盤が挟まれた構造ができあがります。
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilaminar_embryonic_disc
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/embryonic-disc
syncytiotrophoblast 栄養膜合胞体層
blastocyst 胚盤胞の内部細胞塊側に位置する栄養膜細胞層 cytotrophoblastから分化した細胞が、細胞同士が融合し、多核化することによりsyncytiotrophoblast 栄養膜合胞体層(syntrophoblast とも呼ばれる)が生じます(受精後5~6日目)。syncytiotrophoblast 栄養膜合胞体層は最初は部分的ですがやがて胚全体を覆います(受精後11~12日目頃)。もともとblastocystの壁を構成していたtrophoblastの細胞は、そのままそこに残りcytotrophoblastと呼ばれるようになります。
- Carlson Fig.4.20 および 本文
Hatching
blastocystがzona pellucida 透明体を破って外にでることをhatchingと呼びます。
- Carlson Fig.4.3
Implantation is the process of the blastocyst embedding into the endometrial lining of the uterus, which typically occurs in Week 2 of development. For implantation to occur, the blastocyst must completely hatch from the zona pellucida once the conceptus enters the uterine cavity. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554562/
implantation 着床
chorionic cavity 絨毛膜腔もしくはextraembryonic coelom 胚外体腔
受精後12~13日目に、primary yolk sacの膜とcytotrophoblastの壁のとの間(blastocyst cavity胞胚腔)を満たしていたExtraembryonic mesoderm 胚外中胚葉は、2つの部分に分かれます。一部はprimary yolk sacの膜の外側を多い、もう片方はcytotrophoblastの壁の内側に並び、その間には空隙が生まれます。この空隙はchorionic cavity 絨毛膜腔もしくはextraembryonic coelom 胚外体腔と呼ばれます。
- https://www.jpn-ava.com/?tgt=&s=Chorionic+cavity
- 中外医学社 基礎編―人体発生― http://www.chugaiigaku.jp/upfile/browse/browse3399.pdf
secondary yolk sac 二次卵黄嚢
受精の12~13日目ごろに、hypoblast 胚盤葉下層の細胞が移動して新たに卵黄嚢の膜を作ります。もともとあった原始卵黄嚢は押しやられて退化し最終的には消滅します。2次的に作られた黄嚢嚢はdefinitive yolk sacと呼ばれます。
- Larsen FIG.2.3
yolk sac はumbilical vesicleとも呼ばれるようです。
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32310425/ The yolk sac, or umbilical vesicle, is a small membranous structure outside the embryo with various functions during embryonic development. The yolk sac reduces in size, communicates ventrally with the developing embryo via the yolk stalk, and later regresses.
intraembryonic mesoderm 胚内中胚葉
受精後3週めは原腸胚形成の時期です。それまでは、外胚葉と内胚葉からなる二層性胚盤 bilaminar embryonic discの状態だったわけですが、受精後16日目に、epiblast 胚盤葉上層の細胞の一部がhypoblast 胚盤葉下層のほうに向かって移動し、epiblast 胚盤葉上層とhypoblast 胚盤葉下層との間に位置してintraembryonic mesoderm 胚内中胚葉があらたに形成されます。
- Larsen FIG.3.5
gastrulation 嚢胚形成;原腸胚形成
- Embryology: Gastrulation – Let’s Make the Primitive Streak and Germ Layers (1:25:04) Douglas Gillard, DC, Professor of Clinical Science チャンネル登録者数 6.49万人
intraembryonic mesoderm 胚内中胚葉を形成する一連の細胞移動の時期はgastrulation 嚢胚形成;原腸胚形成と呼ばれます。この段階で、外胚葉、中胚葉、内胚葉の3つが出そろって三胚葉の時期ということになります。
- Larsen FIG.3.5
じつは中胚葉だけでなく、embryonic endodermもこのときにepiblastから移動してきた細胞で、hypoblastの細胞と置き換わって同じ場所を占めることになります。これは両生類の発生とはだいぶ異なっていますね。
- Embryology: from Fertilization to Gastrulation, Animation Alila Medical Media チャンネル登録者数 124万人 わかりやすい動画。
- The Process of Gastrulation Primal Pictures 3D Anatomy & Physiology ヒトの胚での原腸胚形成がどのようにして起こるのかがわかりやすいアニメーションで説明されています。このステージで、背腹軸、左右軸が決まります。
- Embryology | Mesoderm (26:55) Ninja Nerd チャンネル登録者数 290万人
論文
- Legier, T., Rattier, D., Llewellyn, J. et al. Epithelial disruption drives mesendoderm differentiation in human pluripotent stem cells by enabling TGF-β protein sensing. Nat Commun 14, 349 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-35965-8
尾芽 tail budと第2次神経誘導
Fate of the Primitive Streak, Teratomas, formation of the Notochord, Diastematomyelia, Chordoma, + Douglas Gillard, DC, Professor of Clinical Science チャンネル登録者数 6.49万人
第4週 胚のディスクの折りたたみ Embryonic folding
それまではディスクの形状だったものが、両端が曲がることによって、筒状へと胚の形が変化します。この包み込み運動(folding)は頭尾軸に関して(craniocaudal folding)と左右軸に関して(lateral folding)の両方で起こります。
- Larsen FIG.4.2
- https://med.uc.edu/landing-pages/embryonic-folding/longitudinal-section このウェブサイトの動画およびその解説がわかりやすいです。どの細胞がどの細胞とつながっているのか、どの空隙がどの空隙がつながっているのかを総括しています。また、フォールディングによってどの端とどの端が結合するのかもわかりやすく解説されています。心臓の周りの空間や腸管の周りの空間がextraembryonic coelomだということがわかります。
- General Embryology – Detailed Animation On Embryonic Folding Medical Animations (2:49)
gut 消化菅とintraembryonic coelom 胚体内体腔
embryonic foldingの結果として、あらたな腔が生じます。下の動画を見るとgutおよびintraembryonic coelomがどうやってできたかが理解しやすいと思います。この動画を見ると、消化菅はyolk sacから形成されており消化管の内腔はyolk sacの内部だったことがわかります。
05 Folding of the Embryo Medical Animations チャンネル登録者数 16.7万人
消化管の外側の空隙がintraembryonic coelom 胚体内体腔ですが、この空間はもともとはextraembryonic coelom (chorionic cavity)に相当していることがわかります。
The extraembryonic coelom, also called the chorionic cavity, is continuous with the intraembryonic coelom along the lateral edge of the embryo, where the lateral plate mesoderm has split into splanchnopleuric and somatopleuric layers.
https://med.uc.edu/landing-pages/embryonic-folding/longitudinal-section
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intraembryonic_coelom
- https://med.uc.edu/landing-pages/embryonic-folding/longitudinal-section
胚を取り囲む膜
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetal_membranes
その他の参考記事
- 早期の人卵に於いて 横尾安夫 日医大誌第24巻第9号(1957年) https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jnms1923/24/9/24_9_591/_pdf