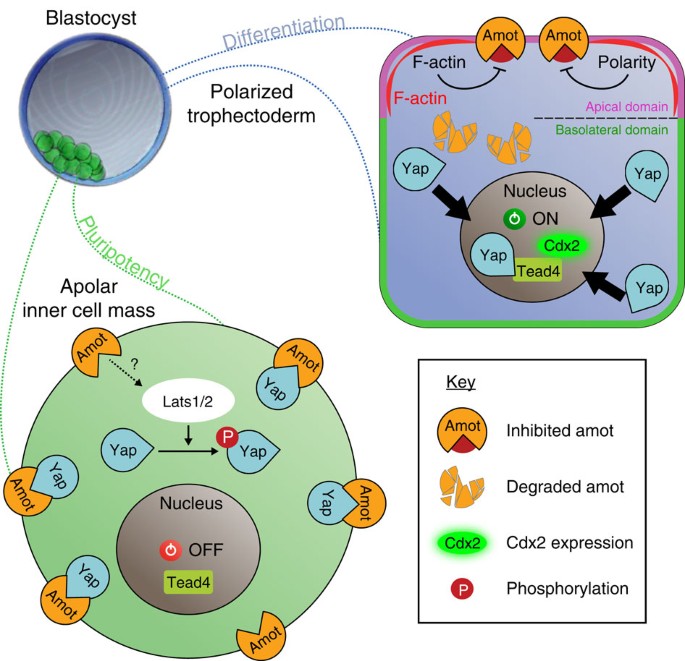
TrophoblastとInner cell massという2つの細胞のタイプへ分化する時にHIPPOシグナル経路が重要で、これが活性化した場合にはLATS1/2キナーゼがリン酸かされて今度はそれが細胞質中に存在する転写因子YAZをリン酸化して、リン酸化YAZは核の中に入れないため、Trophoblastの方には分化しない。一方、Trophoblastになる細胞では、HIPPOが活性化されないため、LATS1/2も活性化されず、YAZもリン酸化されないのでYAZは核内に移行することができてTEAD4という別の転写因子と結合して、Trophoblast特異的な遺伝子(Cdx2など)を発現誘導する。ということが発生学の教科書に書かれています(Carlsonなど)。
しかし、HIPPPOシグナルのオンオフがどのようにして調節されるのかの記述が全くありません。そもそもHIPPOというタンパク質(キナーゼ)に関する記述すらありません。カールソンの発生学の教科書をみると、「上流からのシグナル」がLATSを活性化するという説明をしており、HIPPOがとは書いていないのが、不思議でなりませんでした。あれこれ読み漁っているうちにわかってきたことは、HIPPOシグナル経路といいつつ、初期胚がTrophoblaset (Trophectoderm, TE)とInnser cell mass (ICM)に分化する際にHIPPOシグナル経路を活性化するのはHIPPOではなく、細胞極性だということのようです。桑実胚の外側の割球か内側に位置する割球かによって、細胞接着の状態がことなり、細胞極性の有無も変わるので、それ自体がすでにシグナルとして機能してLATSの活性化につながるということのようですね。
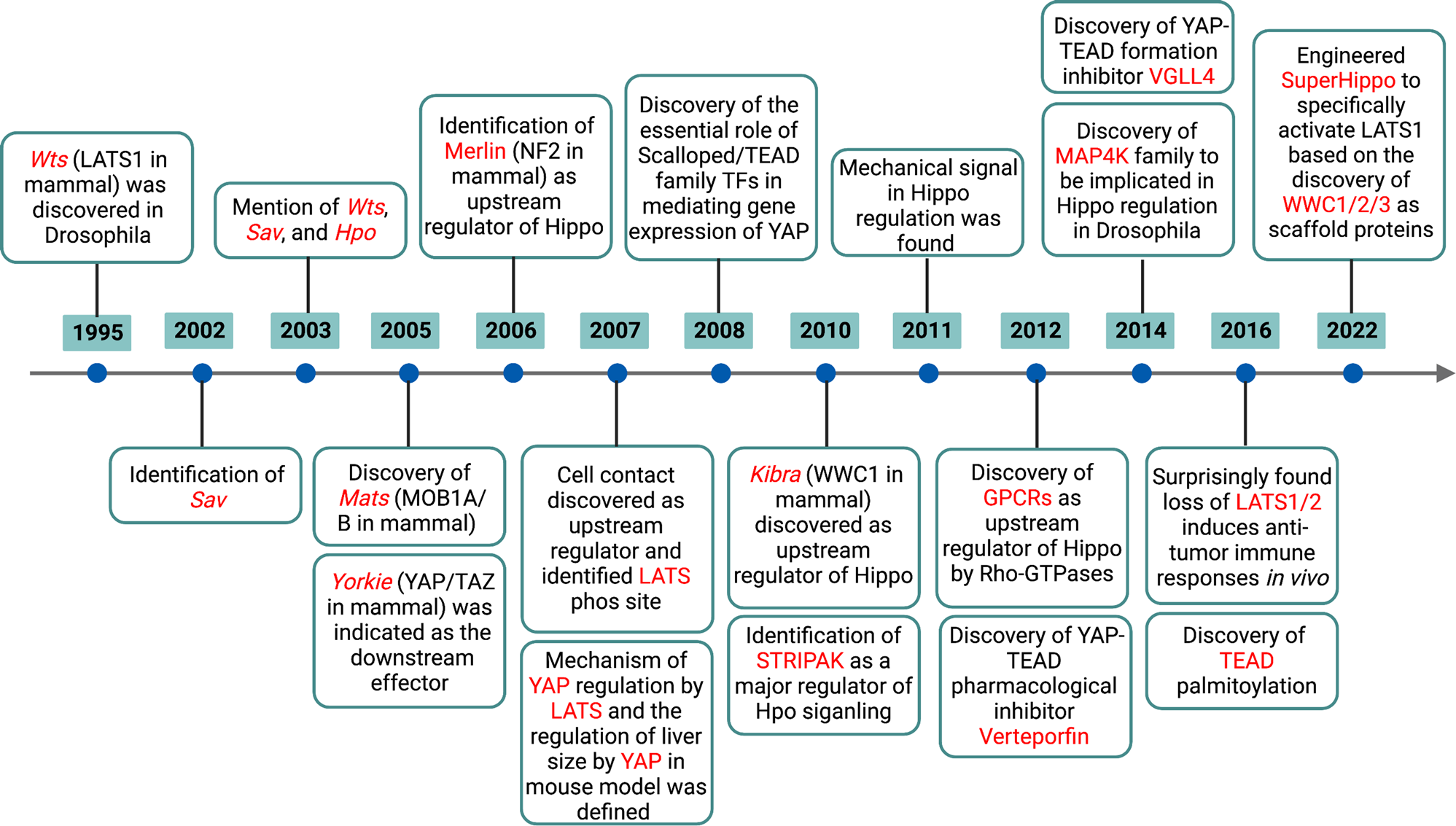
HIPPOシグナリングは、初期胚だけでなく細胞増殖の制御に関わる様々なところで顔を出してきます。がん化においても重要です。クロストークする他のシグナル経路も多く、HIPPOシグナル経路を活性化する上流に位置する刺激も多岐にわたります。
HIPPOキナーゼの変異体の表現型
HIPPOはカバという意味ですが、もともとはショウジョウバエの突然変異体の表現型に対して付けられた名前です。組織の細胞増殖が制御不能になってデカくなってしまったことを描写した名前のようです。哺乳類のオルソログ遺伝子MST1/2の働きを肝臓において破壊してやると(conditional knock out mice)、肝臓がデカくなります。つまり、肝臓においては、肝臓の細胞の増殖を制御しているということがわかります。おそらく、全身でノックアウトすると多分致死なので、コンディショナルノックアウトマウスを作って表現型を調べたのでしょう。
Development 138, 9-22 (2011) doi:10.1242/dev.045500 Hippo signaling: growth control and beyond
HIPPPOシグナリング分子
登場する役者の数があまりにも多くて圧倒されます。下の図を見ると、Lats, Yap, Amot, Mob1,WW45,Kibra,Merlin,Pai,Pals1,Crb1,alpha-cat, 14-3-3, タイトジャンクション構成分子、アドヘレンスジャンクション構成分子といった具合に圧倒されるくらいに多数のタンパク質が関与しています。
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Chapter-2-Merlin-and-Angiomotin-in-Hippo-Yap-Yi-Kissil/8a70d686b3fb97def7e6f4793bff6215d28cd2bc/figure/2
これらの多数の役者たちは、年を追うごとに増えてきました。
08 November 2022 The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-022-01191-9
下はちょっと古くて2009年の論文ですがイントロ部分に役者たちのことが上手くまとまっているおので、頭の整理のために、ちょっと引用しておきます。
- Mst1 and Mst2 are 56–60kDa class 2 GC kinases that share 76% identity in amino acid sequence (Dan et al., 2001).
- Mst1/2 are the closest mammalian homologs of the Drosophila Hippo kinase.
- Loss of Hippo function (in the fly eye) results in massive overgrowth, due to an acceleration of cell cycle progression and a failure of developmental apoptosis (Harvey et al., 2003; Udan et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2003);
- Hippo, when bound to the adaptor protein Salvador/Shar-pei, phosphorylates the Lats/Warts kinase.
- Hippo also phosphorylates the noncatalytic polypeptide, Mats (Mob1 as tumor Suppressor), enabling the latter to promote Lats/Warts autophosphorylation and activation.
- Active Lats/Warts in turn phosphorylates and inhibits the transcriptional coregulator Yorkie, by promoting its binding to 14-3-3 and nuclear exit (Dong et al., 2007).
- The regulation of Hippo kinase activity is less well defined, although elimination of the atypical cadherin, Fat, or both of the FERM domain proteins, Merlin and Expanded, results in Yorkie-dependent phenotypes resembling Hippo loss of function (Reddy and Irvine, 2008).
- the ability of Mst1/2 to phosphorylate Lats1/2 and Mob1, as well as Lats1 phosphorylation and inhibition of Yap1, the mammalian ortholog of Yorkie, have been observed in vitro and in cell culture (Chan et al., 2005; Dong et al., 2007; Hao et al., 2008; Praskova et al., 2008; Zhao et al., 2007).
- cell-cell contact of cultured mammalian cells induces phosphorylation and inactivation of Yap1, whereas overexpression of Yap1 or inactivation of either Lats2 or NF2/Merlin bypasses contact inhibition of growth (McPherson et al., 2004; Morrison et al., 2001; Zhao et al., 2007).
- mouse keratinocytes lacking WW45, the ortholog of Salvador/Shar-pei, fail to activate Mst1, phosphorylate Yap1, and exit the cell cycle during differentiation in vitro (Lee et al., 2008).
- inactivating mutations in NF2 and WW45 have been observed in a number of human cancers and Lats1 knockout mice develop soft tissue sarcomas and ovarian cancers (McClatchey and Giovannini, 2005; McPherson et al., 2004; Tapon et al., 2002).
- Yap1 is amplified in a number of human tumor types and transgenic overexpression of Yap1 in mice leads to liver overgrowth and HCC as well as expansion of progenitor cells in multiple organs (Camargo et al., 2007; Dong et al., 2007; Overholtzer et al., 2006; Zender et al., 2006).
- Mst1 deficient mice exhibit greatly diminished numbers of mature, naïve T cells in peripheral lymphoid organs associated with defects in adhesion and migration of the Mst1 null T cells.
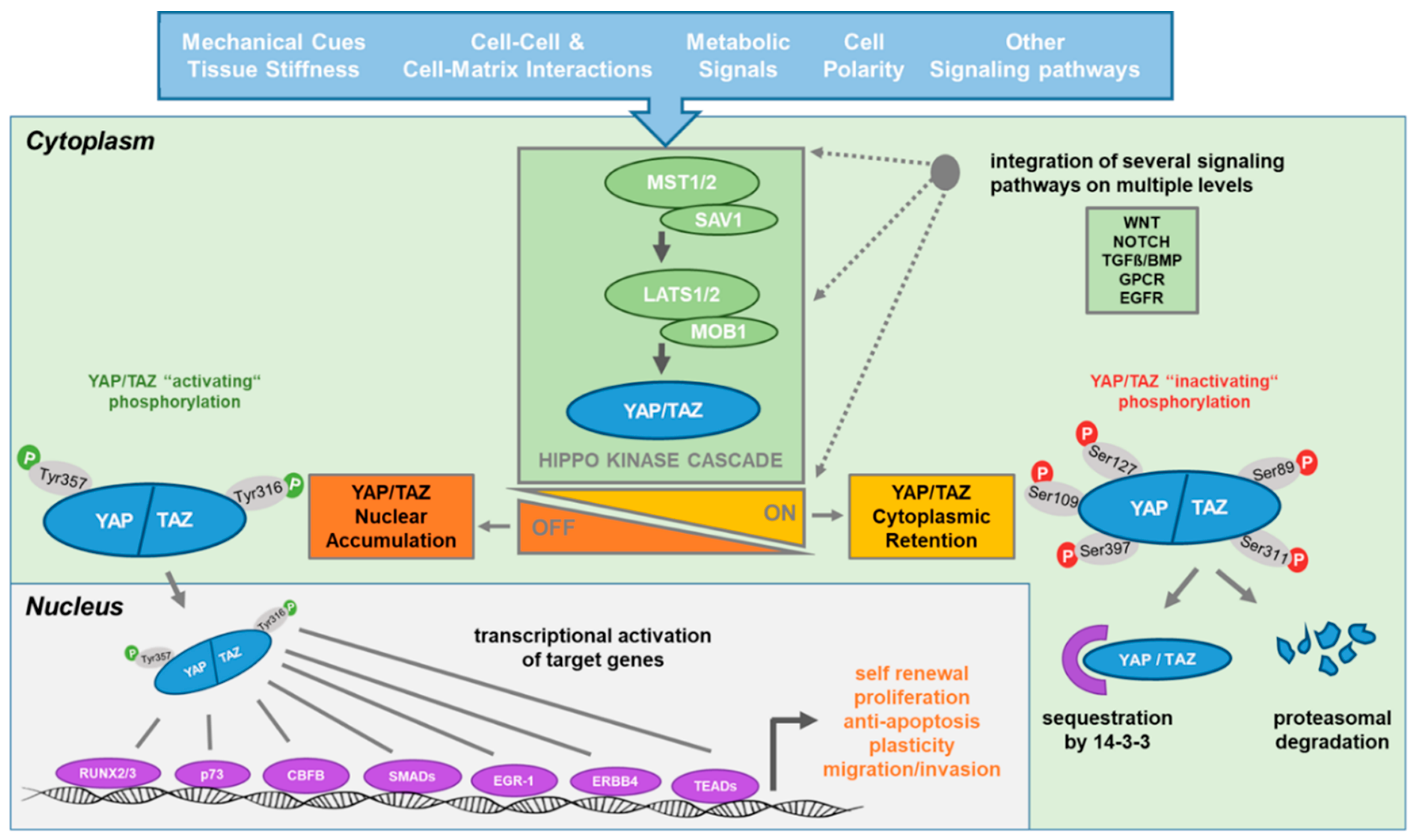
HIPPOシグナリングの主要な部分
文章での説明が分かりやすいものを纏めておきます。
In mammalian cells, MST1/2 (Hippo orthologues) can be activated by several membrane receptors and subsequently phosphorylate downstream kinases LATS1/2 (Warts orthologues) in events that are coordinated by scaffold proteins
MOB1 (Mats orthologue) and WW45 (Salvador orthologue) (16, 17). Activated LATS1/2 can directly phosphorylate YAP1 (Yorkie orthologue) at Ser127, which provides a docking site for 14-3-3 protein and then leads to YAP1 cytoplasmic retention (18). Phosphorylated YAP1 also recruits Skp1/Cul1/F-box protein (SCF)–β-transducing repeat containing protein (β-TRCP) E3 ligase which
promotes YAP1 ubiquitination and degradation in the cytoplasm (19). When YAP1 is in the nucleus, YAP1 binds to transcription factors such as TEA domain transcription
factor (TEAD) and activates the transcription of proliferation and/or survival-related genes (20).dysregulation of YAP1 greatly enhances tumorigenesis because YAP1 not only promotes cell proliferation but also leads to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT),3 which lessens cell contact inhibition and thus allows tumorigenesis (18, 21).
https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(20)56140-1/pdf
When the Hippo pathway is turned on, MST1/2 is phosphorylated and form a complex with SAV1, which phosphorylates and activates the LATS1/2-MOB1 complex. This activated complex then phosphorylates YAP/TAZ resulting in either degradation or cytoplasmic retention leading to reduced nuclear YAP/TAZ levels and down regulation of the downstream targets of this pathway.
During the off-state of the Hippo signaling pathway, unphosphorylated YAP/TAZ translocate to the nucleus and form a complex with TEA domain proteins 1-4 (TEAD1-4) promoting gene expression involved in cell survival, proliferation, and migration.
https://opendata.uni-halle.de/bitstream/1981185920/25548/1/Madencioglu-Kul_Deniz-Ashan-Dissertation_2019.pdf 2019年 博士論文
MST1/MST2 (Mammalian homologues of Drosophila Hippo)
-
The Drosophila Mst Ortholog, hippo, Restricts Growth and Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis Cell Volume 114, Issue 4 , 22 August 2003, Pages 457-467 Here, we describe mutations in hippo (hpo), which encodes a protein kinase most related to mammalian Mst1 and Mst2. Like wts and sav, hpo mutations result in increased tissue growth and impaired apoptosis characterized by elevated levels of the cell cycle regulator cyclin E and apoptosis inhibitor DIAP1. HIPPOを同定した論文!哺乳類のホモログはすでに知られていたのですね。サイクリンEはG1期からS期へ移行するときに必要な分子です。
-
Characterization of Two Mst1-Deficient Mouse Models Dev Dyn. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 May 1. Published in final edited form as:Dev Dyn. 2008 Nov; 237(11): 3424–3434. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21764
YAP/TAZの活性化(核内移行と転写因子としての活性)
簡略化された説明だと、YAPがリン酸化されると分解されるほうこうに向かい、リン酸化されない状態で核内に移行して転写因子として働くとされています。しかし、下のレビュー論文はもっと詳細で、活性化されるときと活性化されないときで、リン酸化されるアミノ酸部位が異なるということのようです。チロシンリン酸化(Tyr316,Tyr357)で活性化され、セリンリン酸化(Ser89, Ser109, Ser127,Ser311, Ser397)で分解される運命に向かいます。
- transcriptional co-activators Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP-1, YAP)
- paralogue, the transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ, WWTR1)
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/9/4/972#B15-cells-09-00972
細胞接着因子―細胞骨格ーHIPPPOシグナリング分子
Kibra
2010年の段階で、Hippono上流にあるシグナル分子としてKibra, Merlin, Expandedが見つかっていますが、Hippoシグナリングをどのように制御しているのかは不明なようです。
The FERM domain proteins Merlin (Mer) and Expanded (Ex) are upstream components that regulate Hpo activity through unknown mechanisms. Here we identify Kibra as another upstream component of the Hippo signaling pathway. We show that Kibra functions together with Mer and Ex in a protein complex localized to the apical domain of epithelial cells, and that this protein complex regulates the Hippo kinase cascade via direct binding to Hpo and Sav.
Kibra Functions as a Tumor Suppressor Protein that Regulates Hippo Signaling in Conjunction with Merlin and Expanded Developmental Cell 18, 288–299, February 16, 2010 https://www.cell.com/developmental-cell/pdf/S1534-5807(10)00006-7.pdf
angiomotin(AMOT) and angiomotin-like proteins
ややこしいですね。Hippoは重要なシグナリング経路かと思いきや、Hippo非依存的な経路としてAMOTが関わる経路があるという論文が出ています。意外性があるからこそのNature Communications論文なのでしょう。
We propose that both Hippo pathway-dependent and Hippo pathway-independent mechanisms regulate Yap localization to set apart pluripotent and differentiated lineages in the pre-implantation mouse embryo.
Leung, C., Zernicka-Goetz, M. Angiomotin prevents pluripotent lineage differentiation in mouse embryos via Hippo pathway-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Nat Commun 4, 2251 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3251 https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms3251
YAP may also be repressed in a phosphorylation-independent manner
in Drosophila (22). In this case, the Hippo pathway components Expanded, Hippo, and Warts can directly bind to YAP1 through physical interaction between their corresponding PY motifs and the WW domains of YAP1.Here, we report the identification of angiomotin (AMOT) and angiomotin-like proteins as new YAP1-associated proteins. AMOT is a vascular angiogenesis-related protein, which was initially identified as an angiogenesis inhibitor angiostatin-binding protein through a yeast twohybrid screen (23, 24).
There are two other angiomotin-like proteins, AMOTL1 and AMOTL2. These three proteins belong to a new protein family with a highly conserved coil-coil domain, PDZ binding domain, and glutamine-rich domain (24).
AMOT, AMOTL1, and AMOTL2 specifically interact with YAP1. This interaction is important for the regulation of YAP1 cytoplasm-to-nucleus translocation. Just like YAP1 overexpression, down-regulation of AMOTL2 in MCF10A cells promotes EMT. Together, these data suggest that YAP1 is regulated in vivo via its directinteractions with angiomotin-like proteins.
https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(20)56140-1/pdf
- The Angiomotins – From discovery to function FEBS Letters Volume 588, Issue 16 , 19 August 2014, Pages 2693-2703 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014579314001252
考えられるシグナルカスケード
ややこしい話ですが、YAPの核移行・細胞質内保持に関するシグナル経路が下の論文では5通りも紹介されています。
Annu Rev Genet. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2019 Nov 23. Published in final edited form as: Annu Rev Genet. 2018 Nov 23; 52: 65–87. Published online 2018 Sep 5. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031621 PMCID: PMC6322405 NIHMSID: NIHMS1002595 PMID: 30183404 The Hippo signaling network and its biological functions
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6322405/
Investigating the role of the Hippo pathway member Nf2 in the segregation of trophectoderm and inner cell mass Katie Cockburn Published 1 November 2015 https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Investigating-the-role-of-the-Hippo-pathway-member-Cockburn/426d8e88f606c02cd4df88bc2a4006b7d42b5b61/figure/3
Overview of junctional complexes during mammalian early embryonic development Frontiers Frontiers in Endocrinology 14 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2023.1150017 https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Differential-modulation-of-the-Hippo-signaling-pathway-in-inner-and-outer-cells-of-the_fig3_370168194
Emerging roles for angiomotin in the nervous system Science Signaling 27 Oct 2020 Vol 13, Issue 655 DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.abc0635 https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scisignal.abc0635
2015年の論文ですが、一番網羅的な図は下の図でしょうか。
DOI:10.1093/abbs/gmu110Corpus ID: 24216059 The regulation and function of YAP transcription co-activator. Chu Zhu, Li Li, Bin Zhao Published in Acta Biochimica et Biophysica… 2015 Biology, Medicine https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-regulation-and-function-of-YAP-transcription-Zhu-Li/1f32caa888a61e0717a5b20d0699d971e1933d17