angiomotin (Amot)は、卵割期の哺乳類胚で栄養層細胞と内部細胞塊に分化する過程でHIPPOシグナリングが働くときに関与する分子として知りましたが、どうしてAmotによって異なる運命に分化していくのかがいまひとつわかりませんでした。
angiomotinの発見のいきさつと名前の由来
- Angiomotin An Angiostatin Binding Protein That Regulates Endothelial Cell Migration and Tube Formation. J Cell Biol. 2001 Mar 19; 152(6): 1247–1254. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.6.1247 PMCID: PMC2199208
Angiomotin was discovered in 2001 by screening a placenta yeast two-hybrid cDNA library for angiostatin-binding peptides, using a construct encoding the kringle domains 1-4 of angiostatin. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiomotin
アンジオスタチンが血管新生抑制作用を発揮する機序との関連で、これまでにアンジオスタチンと結合するタンパクが複数同定されている(4)。‥ アンジオスタチン結合タンパクとして同定されたのがアンジオモーチン(angiomotin)である。アンジオモーチンは675個のアミノ酸で構成される分子量72kDaのタンパクであり、血管内皮細胞に比較的選択的に発現し、focal adhesion kinase(FAK)活性を増強することで内皮細胞の遊走能を促進的に調節する分子であり、アンジオスタチンはこのアンジオモーチンの機能を阻害することが示されている。
アンジオスタチン angiostatin 2015/02/17 作成 日本血栓止血学会
angiomotinのHIPPOシグナリングにおける役割
Consensus.appへの質問:Is the interaction between Angiomotin and actin filaments essential for Hippo pathway regulation?
Consensus.appの回答:これらの研究は、アンジオモチンとアクチンフィラメントの相互作用がヒポ経路の調節に重要であることを示唆しています。 8 papers analyzed, Yes 100%
Angiomotin(Amot)とアクチンフィラメントの相互作用がHippo経路の調節において重要かどうかについての研究は、細胞の増殖、分化、そして生存に関わる重要なメカニズムを解明するための重要なテーマです。Hippo経路は、細胞の接触阻害や組織の大きさの制御に関与しており、Amotの役割はこの経路の中心的な要素とされています。
主要な研究結果
- Amotとアクチンフィラメントの結合とHippo経路の調節:
- Amotのリン酸化とHippo経路の活性化:
- 細胞の位置とHippo経路の調節:
結論
Amotとアクチンフィラメントの相互作用は、Hippo経路の調節において重要な役割を果たしています。LATSキナーゼによるAmotのリン酸化は、アクチンフィラメントとの結合を阻害し、Hippo経路の活性化を促進します。これにより、細胞の増殖や分化が制御され、組織の大きさや細胞の運命が決定されます。したがって、Amotとアクチンフィラメントの相互作用は、Hippo経路の調節において不可欠であると言えます。
参考文献
- Mana-Capelli, S., Paramasivam, M., Dutta, S., & McCollum, D. (2014). Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway signaling. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 25, 1676 – 1685. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E13-11-0701. アンジオモチンタンパク質は、F-アクチン細胞骨格の変化に応じて、Hippo 経路転写共活性化因子 YAP を制御します。
- Chan, S., Lim, C., Guo, F., Tan, I., Leung, T., & Hong, W. (2013). Actin-binding and Cell Proliferation Activities of Angiomotin Family Members Are Regulated by Hippo Pathway-mediated Phosphorylation*. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 37296 – 37307. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.527598. LATS キナーゼによる Amot ファミリー メンバーのリン酸化はアクチン結合を阻害し、Amot を安定化し、細胞増殖を阻害します。
- Hirate, Y., Hirahara, S., Inoue, K., Suzuki, A., Alarcon, V., Akimoto, K., Hirai, T., Hara, T., Adachi, M., Chida, K., Ohno, S., Marikawa, Y., Nakao, K., Shimono, A., & Sasaki, H. (2013). Polarity-Dependent Distribution of Angiomotin Localizes Hippo Signaling in Preimplantation Embryos. Current Biology, 23, 1181-1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.014. Amot の N 末端ドメインは、アクチン結合および Lats タンパク質キナーゼとの相互作用に必要であり、これにより Amot-Lats 相互作用が安定化され、Hippo 経路が活性化されます。
- Mana-Capelli, S., & McCollum, D. (2018). Angiomotins stimulate LATS kinase autophosphorylation and act as scaffolds that promote Hippo signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293, 18230 – 18241. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.004187. アンジオモチンは、LATS1/2 の自己リン酸化を刺激し、LATS1/2 を活性化因子 SAV1-MST1/2 およびその基質 YAP と結び付けることで、Hippo シグナル伝達を強化します。
- Hirate, Y., & Sasaki, H. (2014). The role of angiomotin phosphorylation in the Hippo pathway during preimplantation mouse development. Tissue Barriers, 2. https://doi.org/10.4161/tisb.28127. アンジオモチンのリン酸化は F-アクチンとの相互作用を阻害し、Hippo 経路を活性化して F-アクチンを Lats 活性と結び付けます。
- Li, Y., Zhou, H., Li, F., Chan, S., Lin, Z., Wei, Z., Yang, Z., Guo, F., Lim, C., Xing, W., Shen, Y., Hong, W., Long, J., & Zhang, M. (2015). Angiomotin binding-induced activation of Merlin/NF2 in the Hippo pathway. Cell Research, 25, 801 – 817. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.69. アンジオモチンの結合により自己阻害が解除され、Merlin の Lats1/2 への結合が促進され、完全な Hippo 経路シグナル伝達経路の構築が可能になります。
- Han, Z., Ruthel, G., Dash, S., Berry, C., Freedman, B., Harty, R., & Shtanko, O. (2020). Angiomotin regulates budding and spread of Ebola virus. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 295, 8596 – 8601. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.AC120.013171. アンジオモチンはアクチンの組織化とダイナミクスにおいて役割を果たし、eVP40 を介した退出を促進します。
- Dai, X., She, P., Chi, F., Feng, Y., Liu, H., Jin, D., Zhao, Y., Guo, X., Jiang, D., Guan, K., Zhong, T., & Zhao, B. (2013). Phosphorylation of Angiomotin by Lats1/2 Kinases Inhibits F-actin Binding, Cell Migration, and Angiogenesis*. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 34041 – 34051. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.518019. Lats1/2 によるアンジオモチンのリン酸化は F-アクチンとの相互作用を阻害し、細胞の移動と血管新生を阻害します。
- Zhao, B., Li, L., Lu, Q., Wang, L., Liu, C., Lei, Q., & Guan, K. (2011). Angiomotin is a novel Hippo pathway component that inhibits YAP oncoprotein.. Genes & development, 25 1, 51-63 . https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.2000111. アンジオモチンファミリータンパク質は、タイトジャンクションの局在を介して YAP 腫瘍タンパク質を阻害することにより、Hippo 経路で潜在的な腫瘍抑制の役割を果たします。
- Wigerius, M., Quinn, D., & Fawcett, J. (2020). Emerging roles for angiomotin in the nervous system. Science Signaling, 13. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.abc0635. アンジオモチンファミリーの一員である AMOT-p130 は、正常な脳の発達に不可欠な神経幹細胞の分化、樹状突起のパターン形成、シナプスの成熟において重要な役割を果たします。
angiomotinのHIPPO、LATSを介さないYAP活性化経路
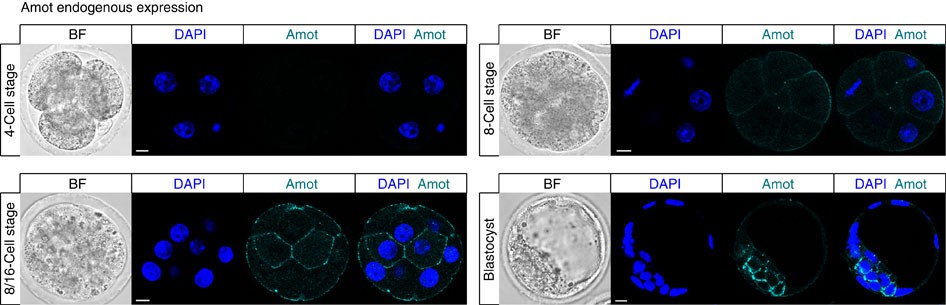
- Angiomotin prevents pluripotent lineage differentiation in mouse embryos via Hippo pathway-dependent and -independent mechanisms C. Leung, M. Zernicka-Goetz Nature Communications https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms3251 https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms3251.pdf 8~16細胞期は全ての割球で発現しているように見えますが、胚盤胞の時期になると内部細胞塊の細胞のみに局在するようです。
angiomotinの多様な役割
- Mihajlović, A., & Bruce, A. (2016). Rho-associated protein kinase regulates subcellular localisation of Angiomotin and Hippo-signalling during preimplantation mouse embryo development. Reproductive biomedicine online, 33 3, 381-90 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2016.06.028. Inhibition of Rho-associated protein kinase (Rock) leads to mislocalization of the Hippo-signalling activator Angiomotin (Amot) to the basolateral regions of outer cells, compromising trophectoderm differentiation.
- Negrón-Pérez, V., & Hansen, P. (2018). Role of yes-associated protein 1, angiomotin, and mitogen-activated kinase kinase 1/2 in development of the bovine blastocyst†. Biology of Reproduction, 98, 170 – 183. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolre/iox172. AMOT protein localization changes from cytoplasmic to nuclear as development advances, and it plays a role in the function of trophectoderm in the bovine blastocyst.
- Hirate, Y., Hirahara, S., Inoue, K., Suzuki, A., Alarcon, V., Akimoto, K., Hirai, T., Hara, T., Adachi, M., Chida, K., Ohno, S., Marikawa, Y., Nakao, K., Shimono, A., & Sasaki, H. (2013). Polarity-Dependent Distribution of Angiomotin Localizes Hippo Signaling in Preimplantation Embryos. Current Biology, 23, 1181-1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.014. In the nonpolar inner cells, Amot localizes to adherens junctions (AJs), and cell-cell adhesion activates the Hippo pathway. In the outer cells, the cell polarity sequesters Amot from basolateral AJs to apical domains, thereby suppressing Hippo signaling. The N-terminal domain of Amot is required for actin binding, Nf2/Merlin-mediated association with the E-cadherin complex, and interaction with Lats protein kinase. In AJs, S176 in the N-terminal domain of Amot is phosphorylated by Lats, which inhibits the actin-binding activity, thereby stabilizing the Amot-Lats interaction to activate the Hippo pathway.
足場タンパク質angiomotin(Amot)およびangiomotin関連AmotL1およびAmotL2がYAPおよびTAZの核転座を阻害することによって、それらの負の調節因子として働いていることが最近明らかになった。一方、Science Signalingの本号においてYiらは、AmotがYAPの核転座を促進し、組織の損傷に対してまたは腫瘍抑制因子Merlin非存在下で、YAP-TEAD複合体の転写補因子として胆管上皮細胞の増殖を促す作用をもつ可能性があることを明らかにした。これらの一見矛盾する結果は、Hippo経路におけるAmotタンパク質に関する理解がまだ限られていることを浮き彫りにしている。
AngiomotinによるYAPの核への移動が細胞増殖および発がんに関与 Angiomotin’g YAP into the Nucleus for Cell Proliferation and Cancer Development Perspectives Sci. Signal., 3 September 2013 Vol. 6, Issue 291, p. pe27 [DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2004573]
- Angiomotin decreases lung cancer progression by sequestering oncogenic YAP/TAZ and decreasing Cyr61 expression. Oncogene 2015 Jul 30;34(31):4056-68. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.333. Epub 2014 Nov 10.