parabiosisの語源
パラバイオ―シスは、語源的には「並んで生きている状態」という意味です。
Excellent etymological question!
You’re absolutely right:
- para- = “beside” or “next to” (παρά)
- bios = “life” (βίος)
So, what about “-sis”?
🔍 “-sis” in Greek
In Greek, “-σις” (-sis) is a noun-forming suffix that denotes:
- action,
- process,
- condition, or
- state of being.
✅ Putting it all together:
parabiosis (παρά + βίος + -σις)
→ literally means:
“the state or condition of living beside (another)”
→ or more loosely:
“a biological state of two lives joined side by side.”
🧠 Similar Greek-derived scientific words using “-sis”:
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| osmosis | process of diffusion through a membrane |
| analysis | the process of breaking up into components |
| diagnosis | the act of identifying a disease |
| synthesis | the process of putting together |
So in parabiosis, the “-sis” makes the whole term into a noun describing a condition or biological process, not just a description of things being “next to each other.”
parabiosisの読み方:パラバイオウシス
How To Say Parabiosis Emma Saying チャンネル登録者数 78.1万人
parabiosisの外科手術
In parabiosis surgery—a procedure where two animals (typically mice) are surgically joined to share a circulatory system—both the epidermis and deeper layers of the skin are sutured, but not just the epithelium.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
✅ What is sutured during parabiosis?
- Skin (including epidermis and dermis):
- The skin is incised and later sutured along the lateral side of each mouse.
- This includes both the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (the deeper layer beneath).
- Proper alignment of the skin layers is important for wound healing and mechanical stability.
- Fascia and possibly muscles:
- The underlying fascia (connective tissue) is usually sutured or stapled together to help the animals stay attached and allow vascular connections to form.
- Sometimes, even the forelimbs or rib cartilage are sutured to stabilize the attachment.
- No direct suturing of blood vessels:
- The circulatory systems are not surgically joined at the blood vessel level; instead, anastomoses (natural vascular connections) form over time.
❗️Clarification on terminology:
- Epithelia of the skin refers to the epidermis, which is epithelial tissue.
- So it’s not that only the epithelium is sutured—rather, the full skin layers (epidermis + dermis) and subdermal tissues are involved.
📚 Reference-style note:
“The skin incisions are sutured with absorbable sutures, and the forelimbs or body walls may be stabilized to promote shared circulation. Over 10–14 days, vascular anastomoses develop, establishing cross-circulation between the animals.”
— Eguchi et al., Nature Protocols, 2015
✅ In parabiosis surgery, only the skin and subcutaneous tissues (like fascia and sometimes muscle) are sutured.
The serosa is not involved, because the peritoneal cavities are not opened.
🧬 To clarify:
| Layer | Sutured? | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Epidermis | ✅ Yes | Outermost epithelial layer of the skin |
| Dermis | ✅ Yes | Connective tissue layer beneath the epidermis |
| Subcutaneous tissue (including fascia) | ✅ Yes | Helps stabilize attachment |
| Muscle (optional) | ✅ Sometimes | Especially near forelimbs or ribs |
| Serosa (e.g., peritoneum) | ❌ No | Not opened or sutured—no entry into abdominal cavity |
🧠 Why not suture the serosa?
- Parabiosis is designed to join the circulatory systems, not the visceral organs.
- Keeping the peritoneal cavities closed avoids complications like infection or peritonitis.
- The vascular anastomoses that eventually form (capillary-to-capillary fusion) occur superficially in the skin and subdermal tissues, not via surgical joining of major vessels or internal organs.
✅ The circulatory system in the skin is located in the dermis, not the epithelium.
🧬 Breakdown of skin layers and circulation:
| Skin Layer | Contains Blood Vessels? | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Epidermis (epithelium) | ❌ No | Avascular (no blood vessels); receives nutrients via diffusion from the dermis |
| Dermis | ✅ Yes | Rich in capillaries, arterioles, venules, and lymphatics |
| Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) | ✅ Yes | Even larger blood vessels and fat tissue reside here |
🩸 How it works:
- The epidermis is nourished by diffusion from capillaries located in the papillary dermis (the upper layer of the dermis).
- Blood vessels in the reticular dermis (deeper layer) help regulate body temperature and provide bulk blood flow.
- No blood vessels ever pass into the epidermis itself.
💡 In parabiosis:
- The vascular anastomoses that form between the two animals arise from capillaries and small vessels in the dermis and hypodermis.
- The epithelial layer is sutured to close the wound, but it plays no role in circulation.
parabiosisの外科手術の実際
Parabiosis in Mice Detailed Experiment Protocol JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments) チャンネル登録者数 2.3万人 有料 無料サンプル2分
parabiosisを用いた研究の隆盛
parabiosisという研究手法は、1950年頃にはブームになったようですが、現在では廃れています。しかしながら、今でもparabiosisを用いた研究成果が論文発表されているので、完全になくなったというわけでもないようです。外科手術だけでできる手軽さがアドバンテージとしてあるせいかもしれません。また「若返り因子」の存在が、parabiosisの実験により明らかにされているにも関わらず、決定打となるような因子の同定には至っていないことも背景としてあるでしょう。
- The term refers to experiments that were first conducted in 1864 by Physiologist Paul Bert. He cut the skin of two mice, then sewed them together. When they healed together their blood vessels combined, enough so that they essentially shared their circulatory systems.
- In the 1950s researchers connected old mice to young mice to determine its effects.
- Parabiosis experiments died out in the 1970s, partly because researchers had learned what they could from the technique, and regulations of animal research made it more challenging to conduct the experiments.
Parabiosis – The Next Snakeoil Steven Novella on August 3, 2016 https://sciencebasedmedicine.org/parabiosis-the-next-snakeoil/
種々のparabiosis研究
下の動画は、説明もうまくて、内容も非常によくまとまっていて勉強になります。
Parabiosis Experiments Prove Bloodborne Aging Factors NutritionFacts.org チャンネル登録者数 126万人
00:56 muscle exchange between old rats and young rats . 若いラットの筋肉細胞を老齢ラットの筋肉に移植すると、老齢化した。逆の組み合わせだと若返った。つまり筋細胞そのものが老化しているのでなく、周囲の環境因子が老齢化に直接的に関わっている。
- 1:11 Nature論文 Rejuvenation of aged progenitor cells by exposure to a young systemic environment 2005. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature03260
- 1:54 Parabiosis . Para = ~ next to . bios = life
- 2:11 シャム双生児
- 2:22 論文 Cojoined twins, conception, pregnancy, and delivery: A reproductive history of the pygopagus Blazek sisters (1878-1922)
- 3:12 Parabiosis between old and young rats Gerontologia 1(1):7-17 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13405201/
parabaiosisは、今の時代は必要なくて、血液に含まれる何か特別な因子の作用を知りたければ、血液だけを取り出して別の個体に輸血すれば済みます。
Can Getting Transfusions of Young Blood Slow Aging? NutritionFacts.org チャンネル登録者数 126万人
パラバイオ―シスを用いた老化研究
Does old blood induce senescence? The Sheekey Science Show チャンネル登録者数 4.58万人
- 老化を制御する液性因子 Humoral factors regulating aging process 新村 健 https://www.jpn-geriat-soc.or.jp/publications/other/pdf/perspective_53_1_10.pdf 1950 年代後半から 1960 年代にかけて,parabiosis(並体結合)といった実験が盛んに行われた.こ れは異なった個体を皮下レベルで手術的に縫合することで,両個体の循環体液を混合して,共有させるといっ た手技である.老齢ラットと若齢ラットの heterochronic parabiosis 研究から,若齢ラットの血中には老 齢ラットを若返らせ,寿命を延長させうる因子が存在することが推測された.さらに抗老化療法であるカロ リー制限を実施したラットと食事自由摂取のラットとの parabiosis 実験から,カロリー制限の好ましい効果 が液性因子によって仲介されるとも推測された.parabiosis による加齢臓器の若返り効果は,骨格筋,軟骨, 肝臓,中枢神経系,心臓と,さまざまな臓器で確認されてきた.さらに動物実験では,輸血や血液成分交換 による若返り効果も数多く報告されている.このような事実から,血液に含まれる何らかの成分が,個体老 化に大きな影響をおよぼしていることは,ほぼ確実と考えられている. 近年,このような老化を促進あるいは抑制する液性因子として,補体 C1q,Growth differentiation factor 11,chemokine ligand 11,β2-microglobulin などが相次いで報告された.
パラバイオ―シスを用いたジストロフィー研究
- 27 April 2020 Heterogenetic parabiosis between healthy and dystrophic mice improve the histopathology in muscular dystrophy Scientific Reports volume 10, Article number: 7075 (2020) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-64042-z
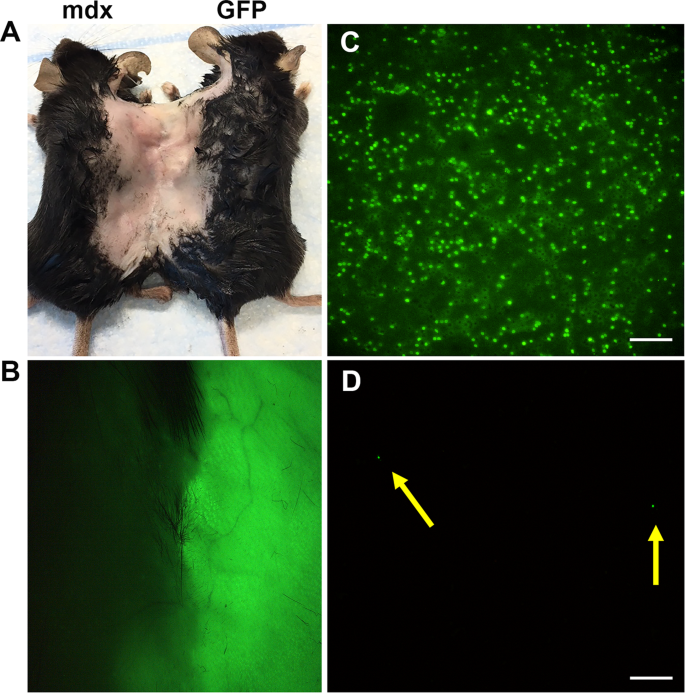 Confirmation of circulatory establishment between parabiotic pairings.
Confirmation of circulatory establishment between parabiotic pairings.
参考ウェブ記事
- 3月6日 またまた細胞老化の体液説(3月2日 Nature オンライン掲載論文) 2022年3月6日 https://aasj.jp/news/watch/19188
- 5月13日老化の体液説(Nature Medicineオンライン版掲載論文) 2014年5月13日 https://aasj.jp/news/watch/1549
- 「若い血」で若返り? 血液研究が教える抗老化薬の可能性 2025.2.10 日経BOOKS PLUS https://bookplus.nikkei.com/atcl/column/012700467/012900005/
- https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/ヴェンカトラマン・ラマクリシュナン