ビタミンCとは
ビタミンCは、ビタミン13種類の中でも一番有名だと思います。メジャーな役割は働きは2つあります。1つめは、有名な抗酸化作用。2つめは、コラーゲンを水酸化(ーOH基をつける)する反応に必要な補酵素として。コラーゲンは水酸化されて初めて正常な機能を持ちます。コラーゲンは、歯肉(歯ぐきのこと)など結合組織を構成する重要な成分。そのため、ビタミンCが欠乏するとコラーゲンが機能しない、すなわち正常な結合組織ができないことになり、非常に重大な結果を引き起こします。ビタミンC欠乏症は、壊血病(かいけつびょう)とも呼ばれ、歯肉炎や皮下出血などの症状を呈します。
壊血病の症状と名前の由来
血管は場所によって太さが違います。細い毛細血管の場合は、一番内側は血管内皮細胞で、その外がわには「血管壁」を構成する細胞があります。血管内日斎藤と血管壁の細胞の間には「基底膜」と呼ばれる膜があり、基底膜はコラーゲンでできています。もっと太い血管の場合は、内膜、中膜、外膜という三層構造をしており、外膜と中膜はコラーゲンやエラスチンでできています。これ‐減は血管を構成する非常に重要なタンパク質なのです。
- カラダをつくり、キレイをつくるコラーゲン 資生堂コラーゲンラボ
壊血病とは血管がもろくなり出血する病気です。口や鼻から多く出血し、いかにも血液が壊れていくような症状であったことから壊血病と呼ばれるようになりました。(ビタミンCの必要性~歴史から見るビタミンC~ 分子生理科学研究所)
- ビタミンC欠乏症(壊血病)(MSDマニュアル家庭版)
- 大航海時代に船員が斃れまくった壊血病~解決したライム野郎って?2022/09/27
補因子としてのビタミンCの働き
ビタミンCは、ジオキシゲナーゼという水酸化酵素の補因子としても重要です。ビタミンC欠乏症(壊血病)で血管がもろくなるのは、血管を構成するコラーゲン繊維ができなくなることが原因です。コラーゲンは、プロリンとリシンが水酸化されることで繊維構造をつくれるようになります。
- ビタミン C は酵素反応の補因子として多様な生理作用を発揮する 2020年
- ビタミンCの真実 東京都健康長寿医療センター研究所 分子老化制御 石神 昭人
細かい話ですが根源的な部分を知れば、全体が統一的に理解できるようになります。まさに生化学は医学の土台ですね。
- ビタミンCはコラーゲンのプロリンとリシンの水酸化に必要な補酵素
- 水酸化されたコラーゲンは3量体を形成して繊維構造をとることができる。
- コラーゲンは結合組織の重要な成分であり、歯ぐき(歯肉)や血管の壁、その他、臓器と臓器、組織と組織を結びつけるような場所に必要。
- ビタミンC欠乏症(壊血病)では、コラーゲンが繊維構造をつくれなくなるため、血管がもろくなり出血しやすくなる。歯ぐきが弱くなり歯が抜ける。
ビタミンCの構造
ビタミンCの構造式をみると、なんとなくグルコースに似ていると感じます。それも当然で、ビタミンCを合成することができる植物や動物(人を含む霊長類は合成できない)は、グルコースを出発材料にビタミンCを作っているから当然、構造が似ているわけです。グルコースの化学式はC6H12O6ですが、ビタミンCの化学式はそれから水素Hが4つなくなっただけでC6H8O6です。
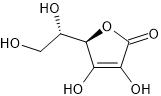 ビタミンC(アスコルビン酸)の構造式(ChemSketchで作成)
ビタミンC(アスコルビン酸)の構造式(ChemSketchで作成)
- 【解ければ化学者】ビタミン C はどれ? ケムステーション
ビタミンCがグルコースからつくられることを知っていれば、上のケムステの問題は超簡単です。
ビタミンCってどんな構造? なぜグルコース(ブドウ糖)に近いの? 他に似たようなものってなに? ビタミンC研究委員会 https://vc-research.info/wisdom/w_01.html
ビタミンC研究の歴史
- 1927年 アルベルト・セント-ジョルジSzent-Györgyiが還元性物質を純粋な結晶として分離し、分子式(C6H8O6)、炭素数6個の糖でかなり強い酸性を示すことからヘキスウロン酸(hexuronic acid)と命名
- 1932年4月 CHEMICAL NATURE OF VITAMIN C C G King, W A Waugh Science 1932 Apr 1;75(1944):357-8. doi: 10.1126/science.75.1944.357-a
- 1932年4月 Hexuronic Acid as the Antiscorbutic Factor J. L. Svirbely, A. Szent-Györgyi Published in Nature 1932 semanticscholar.org
- 1933年 英ハワースがヘキスウロン酸の分子構造を決定し、アスコルビン酸Ascorbic Acidと命名
- 1933年 スイスのタデウシュ・ライヒスタインがビタミンCの化学合成に成功
- 1937年 Nobel Prizein in Chemistry for Haworth
- 1937年 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine for Szent-Györgyi
- なぜ,ビタミンCは,L-アスコルビン酸と呼ばれるの? ビタミンC研究委員会
- https://bronson.co.jp/recommend/history.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213231723001544
- https://www.metrohm.com/ja_jp/discover/blog/2023/history-and-analysis-of-vitamin-c-ascorbic-acid.html
なぜビタミンCの性質を調べたKingとWaughはノーベル賞を受賞しなかったのかと不思議に思ってChatGPTに訊いてみました。
C.G. King and W.A. Waugh were instrumental in the early characterization and isolation of vitamin C, but they were not awarded the Nobel Prize because their contributions were primarily focused on isolation and identification, whereas the Nobel Committee tends to prioritize groundbreaking achievements in synthesis, structural determination, and broader scientific implications.
Key Factors Behind the Nobel Prize Decision:
- Synthetic Achievement and Structural Elucidation:
- Norman Haworth was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1937 for his work in determining the exact molecular structure of vitamin C and related carbohydrates.
- Tadeusz Reichstein synthesized vitamin C chemically (the Reichstein process) in 1933, making large-scale production feasible. This synthesis had significant industrial and public health implications.
- Scope of Contribution:
- While King and Waugh successfully isolated and identified vitamin C from natural sources (such as lemon juice), this was seen as a biochemical characterization rather than a novel synthesis or structural breakthrough.
- The Nobel Committee often emphasizes contributions that lead to new methodologies or synthetic pathways that reshape scientific fields or industries.
- Historical Context and Recognition Bias:
- At the time, there was a greater emphasis on the chemical synthesis and structural analysis of compounds. This might have overshadowed the contributions of researchers focused on biological or nutritional studies.
- Although King and Waugh’s work was crucial, the synthesis by Reichstein and the structural elucidation by Haworth were viewed as the culminating achievements that had broader scientific and practical impact.
Recognition of King and Waugh’s Work:
- C.G. King’s work on vitamin C isolation was widely recognized in the scientific community and contributed significantly to understanding nutrition and preventing scurvy.
- However, in terms of Nobel-level impact, the ability to synthesize vitamin C and understand its exact structure was seen as the critical step forward.
In summary, the Nobel Prize reflected the synthetic and structural breakthroughs rather than the initial isolation and identification of vitamin C, which explains why King and Waugh were not recipients.
タデウシュ・ライヒスタインがノーベル賞受賞者に含まれなかったのも不思議で、訊いてみました。
Interestingly, Tadeusz Reichstein was not awarded the Nobel Prize for his synthesis of vitamin C, despite his groundbreaking contribution to the field of organic chemistry and the industrial production of vitamin C.
Why Wasn’t Reichstein Awarded the Nobel for Vitamin C?
- Focus of Nobel Recognition: In 1937, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Norman Haworth for his work on carbohydrates and the structural elucidation of vitamin C.
- At the same time, Albert Szent-Györgyi received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of vitamin C and its biological functions.
- Reichstein’s synthetic work, while critical, was seen more as a technical and industrial achievement rather than a pioneering physiological or structural discovery.
Why Might Reichstein Have Felt Overlooked?
- The Scale of His Contribution: Reichstein’s synthesis of vitamin C was seen as a significant achievement in organic chemistry, and many considered it on par with or even surpassing the contributions of Norman Haworth and Albert Szent-Györgyi in terms of practical impact.
- Recognition of Others: While Haworth and Szent-Györgyi were recognized, Reichstein’s work was acknowledged more in the industrial and chemical fields rather than in the realm of physiology or structural discovery, which were the focus of the 1937 prizes.
- Technical vs. Scientific Emphasis: The Nobel Committee may have viewed Reichstein’s work as more of a technical achievement, whereas Haworth’s elucidation of vitamin C’s structure was seen as a theoretical breakthrough that aligned more closely with the Nobel’s emphasis on advancing scientific knowledge.
Reichstein’s Nobel Prize (Later Recognition):
- Tadeusz Reichstein eventually received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1950 – but not for vitamin C. He was awarded the prize for his work on the corticosteroid hormones of the adrenal cortex, including the synthesis of cortisone.
- His contributions to steroid chemistry had profound implications for treating conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
Key Takeaway:
Reichstein’s role in vitamin C synthesis was pivotal for public health and industry, but the Nobel Prize for vitamin C was reserved for Haworth and Szent-Györgyi, whose contributions aligned more directly with the Prize’s emphasis on structural elucidation and physiological impact. Reichstein’s later work in hormone synthesis was the achievement that ultimately earned him Nobel recognition.
ReichsteinはビタミンCの合成ではノーベル賞を逃しましたが、その後、糖質コルチコイドの仕事でノーベル賞を受賞していたんですね。一生の間にノーベル賞級の仕事をいくつもしたというのが、圧倒的です。
ビタミンCの生合成
下の図の①がグルコースです。
細胞分化におけるビタミンCの役割
- Ascorbate regulates haematopoietic stem cell function and leukaemogenesis. Nature. 2017; 549: 476-481
- Restoration of TET2 Function Blocks Aberrant Self-Renewal and Leukemia Progression. Cell. 2017; 170: 1079-1095.e20 Notably, exogenous vitamin C promotes DNA demethylation in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) (Chung et al., 2010, Esteban et al., 2010) and dramatically enhances 5hmC levels in a TET-dependent manner (Blaschke et al., 2013, Chen et al., 2013, Yin et al., 2013).