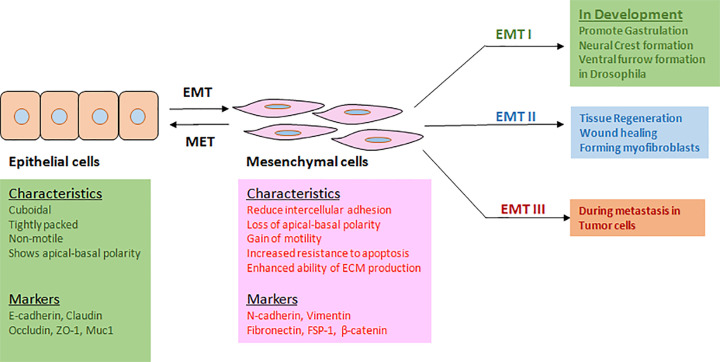
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT)は、上皮間葉転換もしくは上皮間充織転換と訳されますが、上皮系の細胞が間葉系(間充織)の細胞へ分化することを指します。逆に間葉系の細胞が上皮系の細胞に分化することは、mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET)と呼ばれます。両者合わせてEMTと呼ぶこともあるようです。
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease Cell Volume 139, Issue 5p871-890November 25, 2009 https://www.cell.com/fulltext/S0092-8674%2809%2901419-6
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and its transcription factors Biosci Rep. 2021 Dec 23;42(1):BSR20211754. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211754 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8703024/
- Differential Role of Snail1 and Snail2 Zinc Fingers in E-cadherin Repression and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition* J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 1;289(2):930–941. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.528026 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3887216/
During embryogenesis, epithelia are considered to be highly plastic and able to switch back and forth between epithelia and mesenchyme, via the processes of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET), respectively. https://www.jci.org/articles/view/39675
医学の世界では、間葉を、生物学の正解では間充織と言う言葉を用いることが多いようですが、全く同一のものを指します。
そもそも発生学において胚の形成過程を理解するための重要な概念として、「上皮性」細胞と「間葉系」細胞(もしくは間充織細胞)の2者の区別があります。
上皮系の細胞と間葉系の細胞
動物胚を構成する細胞は、形態学的な観点から「上皮性」と「間充織性」の2種類に大別される。上皮性の細胞は一般的に円筒状で、細胞同士が密に接着し、基底膜と呼ばれる細胞外組織の上にシート状に並んでいる。これに対し、間充織細胞は不規則な形態で、細胞同士が部分的に接着し、自由に移動できる運動性をもつ。発生初期では、個々の細胞が増殖、遊走、凝集といった挙動を繰り返しながら位置や形態を変化させ、器官が形づくられていく。興味深い点は、この過程において細胞が2種類の形態を相互に変化させていることだ。特に「上皮性」から「間充織性」へ変化する現象は「上皮‐間充織転換(Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition: EMT)と呼ばれ、原腸形成を始めとする発生時の様々な形態形成過程でみられる。(「上皮‐間充織転換(EMT)」の制御機構に新たな知見 2008年6月23日 独立行政法人 理化学研究所 神戸研究所 発生・再生科学総合研究センター )
- Epithelial to mesenchymal transition during gastrulation: An embryological view Yukiko Nakaya, Guojun Sheng First published: 25 November 2008 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-169X.2008.01070.x Development, Growth and Differentiation (DGD)
発生における上皮間葉転換
Embryonic development depends on epithelial cells changing into migratory mesenchymal cells, and then changing back into epithelial cells when they reach their destination. These interlinked cellular dynamics, termed epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET), have long been recognized as fundamental processes that drive development [1]. https://biosignaling.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12964-021-00761-8
上皮-間葉移行(Epithelial-mesenchymal transition、EMT)は、上皮細胞が間葉系細胞様に形態変化する現象であり、初期胚発生における原腸陥入、神経提細胞の運動や器官形成過程、特に心臓や腎臓での重要性がよく知られている。https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/ja/grant/KAKENHI-PROJECT-19659198/
The transition of epithelial to mesenchymal cells is not irreversible, as several rounds of EMT and MET are necessary for the final differentiation of specialized cell types and the acquisition of the complex three-dimensional structure of internal organs. Accordingly, these sequential rounds are referred to as primary, secondary, and tertiary EMT (Figure 1). (Cell Volume 139, Issue 5, 25 November 2009, Pages 871-890 Review Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease)
Cellular plasticity is fundamental to embryonic development. The importance of cellular transitions in development is first apparent during gastrulation when the process of epithelial to mesenchymal transition transforms polarized epithelial cells into migratory mesenchymal cells that constitute the embryonic and extraembryonic mesoderm. https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1364233269608738688
上皮間葉転換に関わるシグナル分子
上皮間葉転換(epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition:EMT)は,胎児の発生期や創傷の治癒過程で観察される生理学的現象であり,カドヘリンを介して細胞と細胞が接着することによって組織を形成している上皮細胞が,可動性の高い間葉系の細胞に変化する現象を言う.EMT はtransforming growth factor(TGF,トランスフォーミング成長因子)-βファミリーに属する各種因子によって誘導されることが知られている1).炎症,機械的刺激,サイトカインなどが上皮に作用することでもTGF-βの下流シグナルが活性化され,EMT が誘導される.
(上皮間葉転換の腫瘍における意義(PDF) 佐 谷 秀 行 慶應義塾大学医学部先端医科学研究所遺伝子制御研究部門 家族性腫瘍 第10 巻 第2 号 2010 年)
上皮—間葉分化転換とTGF-β
消化管や肺の気道などの管腔は1層の上皮細胞という細胞によって覆われています。80%以上のがんはこの上皮細胞から起こると言われています。上皮細胞はさまざまな刺激で間葉系細胞と呼ばれる細胞に分化し、これを上皮—間葉分化転換(EMT)と呼びます。上皮細胞は丸い形をして細胞同士が固く接着し合っていますが、間葉系細胞は紡錘形の形をしており、細胞同士の接着が弱くなります(図1)。間葉系細胞は上皮細胞に比べて運動する能力が活発であるのが特徴です。EMTは私たちの身体ができる発生の過程で見られますが、上皮細胞ががん細胞に移行していく際に見られる重要な現象でもあります。EMTはさまざまな刺激で起こると考えられていますが、なかでもTGF-βが上皮細胞に作用するとEMTが起こりやすくなります。しかしすべての上皮細胞にTGF-βを加えても一様にEMTが起こる訳ではありません。私たちは膵臓がんの細胞を用いた実験で、膵臓がん細胞にRasというがん遺伝子に異常が起こっていると、TGF-βを加えた場合にEMTが強く見られることを発見しました(がんの浸潤と転移のシグナルネットワークを探る(PDF) 東京大学大学院 医学系研究科 分子病理学分野 宮 園 浩 平)
上皮間葉転換とがん
EMTは発生のときに重要であるだけでなく、がんにおいても重要な意味を持ちます。
EMTには,①発生の過程,②がん化過程,③そして炎症に伴う上皮細胞の間葉系細胞への変換,すなわちColⅠ産生性線維芽細胞・筋線維芽細胞への移行という3種類が存在するとされている.(上皮間充織転換 実験医学ONLINE)
泌尿器形成におけるMET
- Thomas J. Carroll, Joo-Seop Park, Shigemi Hayashi, Arindam Majumdar, Andrew P. McMahon, Wnt9b Plays a Central Role in the Regulation of Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transitions Underlying Organogenesis of the Mammalian Urogenital System, Developmental Cell,Volume 9, Issue 2,2005,Pages 283-292,ISSN 1534-5807, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.05.016.
レビュー論文
- EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer 21, 325–338 (2021). Lambert, A.W., Weinberg, R.A. Linking https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00332-6
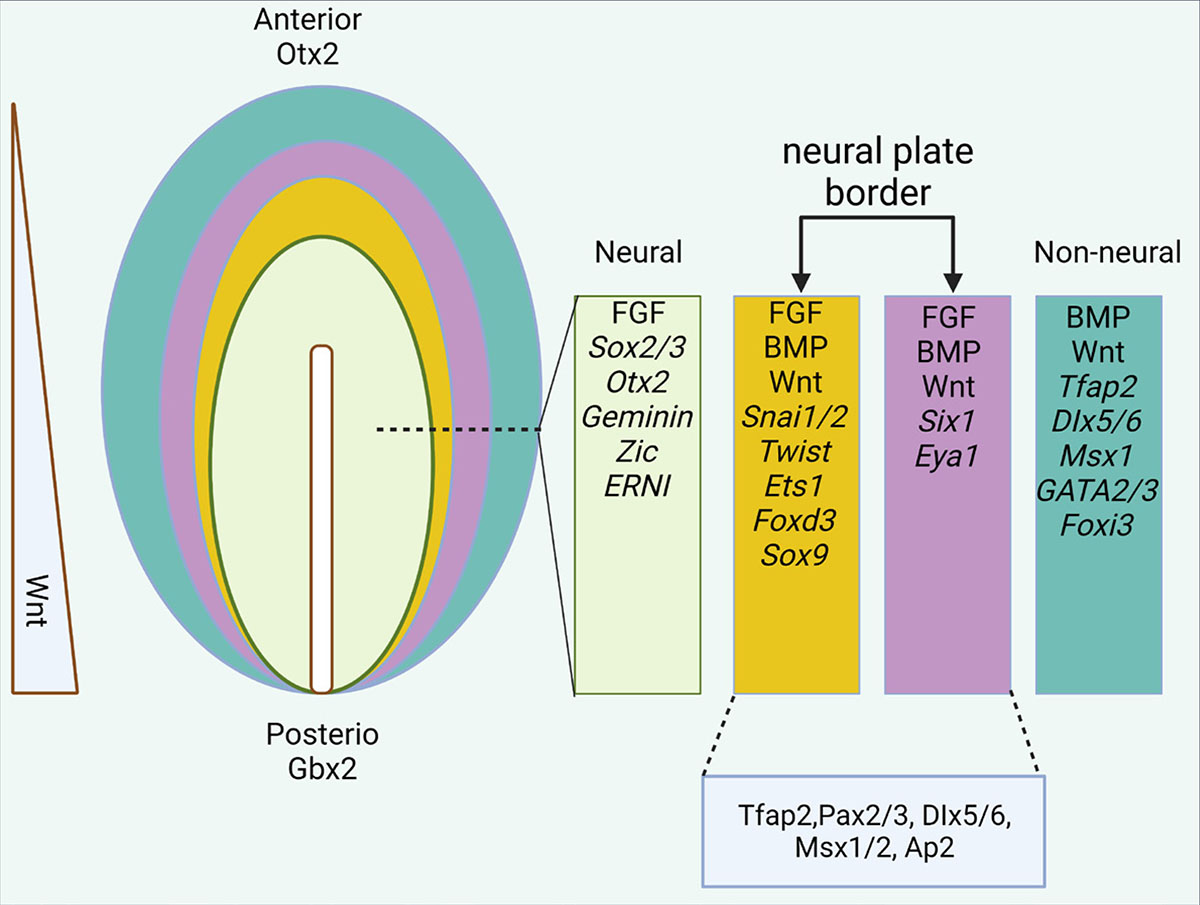
Molecular signaling directing neural plate border formation Int. J. Dev. Biol. 68: 65 – 78 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.230231me Vol 68, Issue 2https://ijdb.ehu.eus/article/230231me