人間はなぜ眠るのか?は未だに明らかになっていない謎だそうです。ただし眠らないとだめという研究はあるそう。
下の動画は睡眠の第一人者が、自身の研究キャリアを交えて睡眠研究の現状を解説していて非常に面白いものです。
【最先端!快眠の科学】Google賞金4.5億!天才睡眠学者が登場【常識覆す研究】 ReHacQ−リハック−【公式】 チャンネル登録者数 93.9万人
1983年RechtscaffenらがScience誌に報告した研究では、「断眠装置」をつくってラットにてきようしたところ、3週間すると、食べているのに体重が減り、体温も低下して死んでしまったそう。少なくとも睡眠は生存に必須と言えそうです。
- Physiological Correlates of Prolonged Sleep Deprivation in Rats ALLAN RECHTSCHAFFEN, MARCIA A. GILLILAND, BERNARD M. BERGMANN, AND JACQUELINE B. WINTERAuthors Info & Affiliations SCIENCE 8 Jul 1983 Vol 221, Issue 4606 pp. 182-184 DOI: 10.1126/science.6857280
眠るといっても身体的な睡眠である必要はなく、脳が眠りさえすればいいみたいです。面白いのはオットセイの睡眠で、左側の脳と右側の脳とは交代交替に眠ることができるのだそう。
REM睡眠とノンREM睡眠
ヒトのREM睡眠は1953年に初めて報告されました(Science誌)。その後、ネコでもREM睡眠が存在することが1958年に報告されています。
- Sleep architecture: REM sleep and Non-REM sleep and sleep stages https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sleep-architecture-REM-sleep-and-Non-REM-sleep-and-sleep-stages-Based-on-29_fig2_221054769
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rapid_eye_movement_sleep
- Regularly Occurring Periods of Eye Motility, and Concomitant Phenomena, During Sleep EUGENE ASERINSKY AND NATHANIEL KLEITMANAuthors Info & Affiliations SCIENCE 4 Sep 1953 Vol 118, Issue 3062 pp. 273-274 DOI: 10.1126/science.118.3062.273
人間が睡眠中に夢をみるのは、REM睡眠中だと言われています。夢を見ているのに実際には体を動かすことはないのが不思議ですが、体あ動かないことをatoniaというそうです。
睡眠(ノンREM睡眠)の役割
睡眠の役割としてこれまでいわれているのは、成長ホルモンは睡眠中に分泌が上昇するということ、ストレスホルモンの分泌は低下するということが知られています。
- Growth hormone secretion during sleep Y. Takahashi, … , D. M. Kipnis, W. H. Daughaday Published September 1, 1968 Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 1968;47(9):2079-2090. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI105893.
- Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol . 1997 Sep;103(3):405-8. doi: 10.1016/s0013-4694(97)00013-1. Temporal relationships between pulsatile cortisol secretion and electroencephalographic activity during sleep in man C Gronfier 1, R Luthringer, M Follenius, N Schaltenbrand, J P Macher, A Muzet, G Brandenberger PMID: 9305289.
また、記憶(シナプスの可塑性)が関係しそうだということ脳の老廃物の除去に関連するのではないかという報告もあります。
- Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain Lulu Xie 1, Hongyi Kang, Qiwu Xu, Michael J Chen, Yonghong Liao, Meenakshisundaram Thiyagarajan, John O’Donnell, Daniel J Christensen, Charles Nicholson, Jeffrey J Iliff, Takahiro Takano, Rashid Deane, Maiken Nedergaard Science . 2013 Oct 18;342(6156):373-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1241224.
- Sleep promotes branch-specific formation of dendritic spines after learning Guang Yang, Cora Sau Wan Lai, Joseph Cichon, Lei Ma, Wei Li, Wen-Biao Gan Science . 2014 Jun 6;344(6188):1173-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1249098.
REM睡眠の役割に関してはほとんどわかっていないようです。
REM睡眠を司る脳の部位はどこか
ネコの脳を脳幹を残してその上部(大脳皮質など)を切って除いた「除脳ネコ」(Pontine cat)を使った実験により、脳幹さえのこっていればREM睡眠が生じるということがJouvetらによって1962年にしめされました。
- Arch Ital Biol . 1962:100:125-206. [Research on the neural structures and responsible mechanisms in different phases of physiological sleep] [Article in French] M JOUVET PMID: 14452612
じゃあ脳幹の中のどの部分がREM睡眠に関係しているのかというと、脳幹の橋(きょう)と呼ばれる部位にある青斑下核α(Peri-LC α)というニューロンがREM睡眠中になると活動するということがわかりました。
- Arch Ital Biol . 1989 Jun;127(3):133-64. Mapping of cholinoceptive brainstem structures responsible for the generation of paradoxical sleep in the cat G Vanni-Mercier 1, K Sakai, J S Lin, M Jouvet https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2774793/ a high amount of paradoxical sleep (PS) was induced by carbachol applications with short latencies, less than 5 minutes, is the mediodorsal pontine tegumentum, namely the nuclei locus coeruleus (LC) alpha and peri-LC alpha, where ChAT-and TH- immunoreactive neurons are intermingled.
- Mapping neuronal inputs to REM sleep induction sites with carbachol-fluorescent microspheres J J Quattrochi 1, A N Mamelak, R D Madison, J D Macklis, J A Hobson Science 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):984-6. doi: 10.1126/science.2475910. The cholinergic agonist carbachol was conjugated to latex microspheres that were fluorescently labeled with rhodamine and used as neuroanatomical probes that show little diffusion from their injection site and retrogradely label neurons projecting to the injection site. Microinjection of this pharmacologically active probe into the gigantocellular field of the cat pontine brain stem caused the awake cats to fall into rapid eye movement (REM) sleep indistinguishable from that produced by free carbachol.
ネコと齧歯類とはすこし事情が異なるようで齧歯類においてはsublaterodorsal nucleus (SLD)と呼ばれる領域がREM睡眠に関与しているようです。ラットを用いた実験で、神経毒によってこの部位を破壊してやるとREM睡眠が減少したという報告があります。
- A putative flip-flop switch for control of REM sleep Jun Lu 1, David Sherman, Marshall Devor, Clifford B Saper Nature . 2006 Jun 1;441(7093):589-94. doi: 10.1038/nature04767. Epub 2006 May 10. PMID: 16688184 DOI: 10.1038/nature04767 Figure 3: The interrelationship of the two halves of the REM switch.
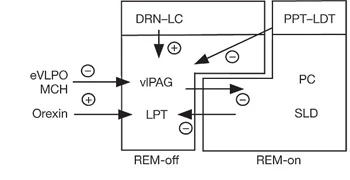
REM睡眠に関与する脳部位はほかにもいくつも発見されており、どれが重要なのかが混沌とした印象です。
- Chung, S., Weber, F., Zhong, P. et al. Identification of preoptic sleep neurons using retrograde labelling and gene profiling. Nature 545, 477–481 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22350 Electrophysiological recordings and c-Fos immunohistochemistry have shown the existence of sleep-active neurons in the preoptic area, especially in the ventrolateral preoptic area and median preoptic nucleus.
- Weber, F., Chung, S., Beier, K. et al. Control of REM sleep by ventral medulla GABAergic neurons. Nature 526, 435–438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14979 Transection studies by Jouvet first demonstrated that the brainstem is both necessary and sufficient for REM sleep generation, and the neural circuits in the pons have since been studied extensively. The medulla also contains neurons that are active during REM sleep, but whether they play a causal role in REM sleep generation remains unclear. Here we show that a GABAergic (γ-aminobutyric-acid-releasing) pathway originating from the ventral medulla powerfully promotes REM sleep in mice.